|
 Course Instructions - READ FIRST Course Instructions - READ FIRST |
|
|
 Course Syllabus Course Syllabus |
|
|
 Course Objectives | Research | Materials Course Objectives | Research | Materials |
Course Outcomes:
- Analyze lesson components to identify embedded best practices that support the diverse language needs of their ELL students.
- Apply best practices to unit and lesson plans.
- Communicate and summarize what best practice strategies are and how they are taught.
- Use best practices in combination with pertinent lesson components and Common Core Standards as they apply specifically to ELLs.
- Apply management strategy with content goals based on industry best practices for inclusive grade-level settings focused on ELL growth.
- Create, scaffold, and differentiate lessons and lesson supports for ELLs.
- Differentiate and scaffold for ELL struggling readers.
- Apply behavior management strategies and how to organize physical space that contributes to an effective classroom environment to real classroom settings, and report back on the experiences.
- Study and practice with successful attributes of student peer review that leads to organized and peaceful transitions and student collaboration.
- Work directly with students to develop a successful multi-cultural classroom environment.
- Design culturally relevant curriculum, with access to culturally relevant resources and materials.
- Apply working knowledge of cultural competence, with an understanding of cultural identity that affects learning, student academic achievement, and overall K-12 pedagogy.
- Describe what racism, stereotyping, and cultural discrimination looks like in teaching, learning and assessment of learning.
- Communicate, summarize, and articulate the relationships among language, bias, and culture in students from diverse backgrounds and at various levels of English language proficiency.
TEXTS, READINGS, INSTRUCTIONAL RESOURCES:
- Ariza, E. N. (2010). What every classroom teacher needs to know about the linguistically, culturally, and ethnically diverse student (2nd ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson
- Behazadi, A. and Sayadian, S. (2015) The Relevance of SLA Research to Language Teaching from Teachers‟ Perspective. International Journal of Educational Investigations Vol.2, No.1: 19-24, 2015, (January).
- Martiniello, M. (2008). Language and the performance of English language learners in math word problems. Harvard Educational Review, 78, 333-368.
- Paradis, J. (2005). Grammatical morphology in children learning English as a second language: Implications of similarities with specific language impairment. Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools, 36, 172-187.
- Wright, W. (2015). Foundations for Teaching English Language Learners: Research, Theory, Policy, and Practice, 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Caslon Publishing.
- Marzano, R. J. (2015). Creating and Using Learning Targets & Performance Scales: HowTeachers Make Better Instructional Decisions. Marzano Laboratories.
- Marzano, R. J. (2012). Becoming a Reflective Teacher. Marzano Laboratories.
- Marzano, R. J. (2015). Processing New Information: Classroom Techniques to Help Students Engage with Content. Marzano Laboratories.
|
|
| Module 1 |
 Plagiarism Policy Plagiarism Policy |
Read and acknowledge this policy by responding to the forum above. |
|
 Understanding Other Cultures Understanding Other Cultures |
|
|
| Module 2 |
 Interests and Learning Styles Interests and Learning Styles |
|
|
| Module 3 |
 Capitalizing on Cultural Backgrounds Capitalizing on Cultural Backgrounds |
|
|
 VIDEO: Confluence of Cultures - Grades 6-12 VIDEO: Confluence of Cultures - Grades 6-12 |
This film was created by Avery Caudill, 18 year old graduate of the Palouse Prairie Charter School in Moscow, ID, an EL Education school. It features fourth graders building and gifting a canoe for and with the Nez Perce tribal organization Nimi´ipuu Protecting the Environment (NPE) who will use it in their educational programs for tribal and non-tribal youth into the future. The students also engaged in environmental service with NPE as part of Better World Day, grounded in their study of the impact of colonization as part of their year-long expedition. |
|
 VIDEO: Teaching Culture Through Music - All Grades VIDEO: Teaching Culture Through Music - All Grades |
Highline teachers Steve Owen and Michelle Crain demonstrate how they adapt lessons and content in response to student voice, cultural diversity, and learning needs. Teachers communicate high expectations for all students and provide the support every student needs to meet them. |
|
| Module 4 |
 Cultural Awareness and Bias in Assessments Cultural Awareness and Bias in Assessments |
|
|
 Checklist for an Anti-Bias Learning Environment Checklist for an Anti-Bias Learning Environment |
What does this checklist from the Anti-Defamation League tell us about bias that we might not be aware of? How can this be used as a tool for our own classrooms? |
|
| Module 5 |
 Culturally Compatible Environments That Foster Learning Culturally Compatible Environments That Foster Learning |
|
|
 English Language Learners' Program Handbook - FL DOE English Language Learners' Program Handbook - FL DOE |
|
|
| Module 6 |
 Classroom Linguistic Routines Classroom Linguistic Routines |
|
|
| Module 7 |
 Theories of Language Acquisition and Differentiation for ELLs Theories of Language Acquisition and Differentiation for ELLs |
|
|
 Integrating Culture into Language Learning Integrating Culture into Language Learning |
|
|
 Ethnic Diversity in Materials Science and Engineering Ethnic Diversity in Materials Science and Engineering |
Ethnic Diversity in Materials Science and Engineering, https://nsf.gov |
|
 Blog About and Share a Content Area Language Resource for Second Language Learners Blog About and Share a Content Area Language Resource for Second Language Learners |

Whether a new literacy resource, a differentiated resource, a resource for inclusive classrooms, or one focused specifically on cross-cultural communication, let's share a resource and talk about it in this blog.
- First, tell us why you chose the resource.
- Next, provide us with a link to the resource and a brief description of it.
- Explain how the resource works effectively, or has the potential to work effectively, with struggling readers.
|
|
 Blogging Instructions Blogging Instructions |
|
|
 Differentiating Instruction for English Language Learners - K-12 Differentiating Instruction for English Language Learners - K-12 |
Veteran teachers Larry Ferlazzo and Katie Hull Synieski offer tips on differentiating instruction for English-language learners. By using techniques such as pairing up students and enhancing background knowledge, teachers can make a lesson accessible to every student in the class, regardless of language proficiency. “Not everybody will get the same exact text or use the same strategy,” Hull Sypnieski explains, “but it’s fair because you’re meeting every student where they are." |
|
 Adapting Curriculum to Learners' Needs Adapting Curriculum to Learners' Needs |
This video illustrates how Kerry Meehan, a third-grade teacher at the World of Inquiry School #58 in Rochester, New York, adapts and differentiates a close reading lesson from an EL Education curriculum module. Meehan attends to students' various readiness levels through her instructional decisions, the adaptation of materials, and classroom management strategies. |
|
| Module 8 |
 Scaffolding Reading and Writing for ELLs Scaffolding Reading and Writing for ELLs |
|
|
 VIDEO: Scaffolding Literacy - Grade 7 VIDEO: Scaffolding Literacy - Grade 7 |
 Examine how literacy is scaffolded for these second language learners. What themes are common to what you have learned in this course so far? Examine how literacy is scaffolded for these second language learners. What themes are common to what you have learned in this course so far?
|
|
 VIDEO: Implementing a Language Dive - K-12 VIDEO: Implementing a Language Dive - K-12 |
See the rigor and joy of Language Dives in a fourth grade classroom at Lead Academy in Greenville, SC. During a Language Dive, teachers and students slow down to have a conversation about the meaning, purpose, and structure of a compelling sentence from a complex text and topic, in this case, the American Revolution. Following the engaging deconstruct-reconstruct-practice routine, students play with the smallest "chunks" of the sentence, acting them out, rearranging them, or using them to talk about their own lives. For more on Language Dives and Conversation Cues, also watch Behind the Practice: Approaching Language Dives with Sarah Mitchell, Stephanie Clayton, and Sloane Young, Small Group Language Dive - Long Version, and Supporting English Language Learners through the Curriculum and Beyond. |
|
| Module 9 |
 Struggling Learners Struggling Learners |
|
|
 VIDEO: Scaffolding Literacy Instruction for English Language Learners - All Grades VIDEO: Scaffolding Literacy Instruction for English Language Learners - All Grades |
Caitlin LeClair, seventh-grade social studies teacher at King Middle School in Portland, Maine, supports her students to read complex texts—fiction and nonfiction—about South Sudan. LeClair supports her diverse group of learners by choosing compelling topics; working through a progression of increasingly complex texts; and providing scaffolding and support to build their skills as close readers. |
|
| Module 10 |
 Behavioral Supports Through Grouping and Collaboration Behavioral Supports Through Grouping and Collaboration |
|
|
 Functional Behavior Checklist Functional Behavior Checklist |
|
|
 FBA Summary FBA Summary |
|
|
 VIDEO: Debrief Circles - Grades K-6 VIDEO: Debrief Circles - Grades K-6 |
Students learn by doing at EL Education's network of more than 160 schools. Math, science, and other subjects are taught through "expeditions" that connect them to their communities and teach them the value of service. Students are encouraged to have "academic courage," and they work alone and in groups to conduct original research, analyze data, and present their findings. The work goes in stages as students solicit feedback and make revisions along the way. Each step in the process reinforces a culture of continuous improvement and refinement. |
|
| Module 12 |
 Engaging 21st Century Learners Engaging 21st Century Learners |
- Introduction: Engaging Learners
- 21st century Tools
|
|
 Brain-Compatible Learning Strategies for ELLs Brain-Compatible Learning Strategies for ELLs |
|
|
 21st Century Resources 21st Century Resources |
Free digital resources for planning and implementation! |
|
| Module 13 |
 VIDEO: SIOP -Sheltered Instruction VIDEO: SIOP -Sheltered Instruction |
 Watch this video to learn what the SIOP model is all about. The video is a little over one hour. Watch as much of it as you need to in order to understand what the SIOP model involves. You will design a SIOP lesson after responding in the forum that follows. Watch this video to learn what the SIOP model is all about. The video is a little over one hour. Watch as much of it as you need to in order to understand what the SIOP model involves. You will design a SIOP lesson after responding in the forum that follows.
|
|
 SIOP Guide SIOP Guide |
Use this Sheltered Instruction Protocol Handbook to guide your responses in the following FORUM: SIOP discussion.
|
|
| Module 14 |
 Adopting and Adapting Adopting and Adapting |
|
|
 Text and Non-Text Selection Criteria Text and Non-Text Selection Criteria |
|
|
| Module 15 |
 Progression and Relevance Progression and Relevance |
Use the PARCC Model Frameworks to develop a language lesson using the ESOL Planning template.
- Identify a grade level to focus on.
- Review at the grade level ELA Model Content Framework Chart in each document (around page 52).
- Look at the progression and how the expectations heighten between grades. For example:
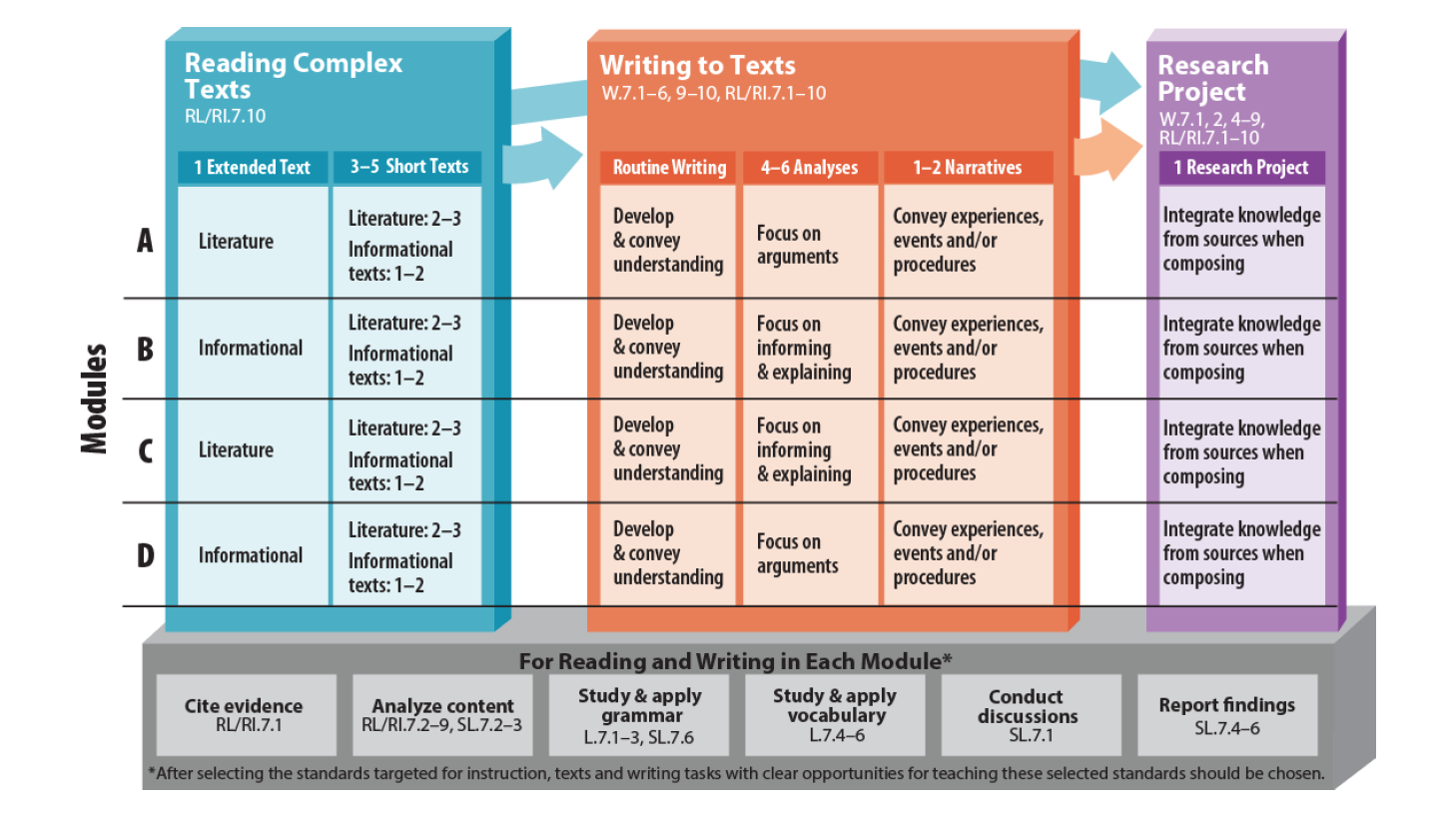
- Consider the needs of your ELLs.
- Consider cultural relevance in curriculum.
- Make applicable content adjustments to include cultural relevance with grade progression.
|
|
 Model Content Frameworks for Mathematics Curriculum Grades 3-11 Model Content Frameworks for Mathematics Curriculum Grades 3-11 |
|
|
 Model Frameworks for ELA Curriculum Grades K-2 Model Frameworks for ELA Curriculum Grades K-2 |
|
|
 Model Frameworks for ELA Curriculum Grades 3-11 Model Frameworks for ELA Curriculum Grades 3-11 |
|
|
 Model Frameworks for Mathematics Curriculum Grades K-2 Model Frameworks for Mathematics Curriculum Grades K-2 |
|
|
| Module 16 |
 Selecting and Modifying Materials to Differentiate Selecting and Modifying Materials to Differentiate |
|
|
 ESOL Planning Template ESOL Planning Template |
|
|
 Module 16 Materials Module 16 Materials |
- Task Modifications Checklist
- Assessment Modifications Checklist
- Modifications to Text Dependent Questions Checklist
|
|
| Module 17 |
 Higher-Order Pedagogies Higher-Order Pedagogies |
|
|
| Module 18 |
 Home, the Family, and Language Development Home, the Family, and Language Development |
|
|
| Module 19 |
 Differentiating Instruction for a Successful Class Environment Differentiating Instruction for a Successful Class Environment |
|
|
 Total Physical Response Total Physical Response |
|
|
 Critical Literacy Strategies Critical Literacy Strategies |
Peruse these resources for more ways to integrate background experience, culture, and prior knowledge into a culturally responsive curriculum. |
|
 VIDEO: Crew Support for Learning - All Grades VIDEO: Crew Support for Learning - All Grades |
- Crew—both the culture and structure of Crew—can be a powerful force to improve academics for students. The essence of Crew in academics is that we are getting smarter together, pushing and supporting each other to understand concepts more fully, be more resilient thinkers and workers, have a growth mindset, work reflectively. It is the ethic of supporting each other all day long—being “Crew” in encouraging, critiquing, and assisting other students in their learning.
|
|
| Module 20 |
 Other ESOL Resources Other ESOL Resources |
|


 Examine how literacy is scaffolded for these second language learners. What themes are common to what you have learned in this course so far?
Examine how literacy is scaffolded for these second language learners. What themes are common to what you have learned in this course so far? Watch this video to learn what the SIOP model is all about. The video is a little over one hour. Watch as much of it as you need to in order to understand what the SIOP model involves. You will design a SIOP lesson after responding in the forum that follows.
Watch this video to learn what the SIOP model is all about. The video is a little over one hour. Watch as much of it as you need to in order to understand what the SIOP model involves. You will design a SIOP lesson after responding in the forum that follows.