Interests and Learning Styles
no insert
3. Learning Style Inventories
Learning Style Inventories:
- Edutopia: What's Your Learning Style?
- Kolb's Learning Styles
- What's Your Learning Style?
- Memletics LS Questionnaire
Differentiating instruction also involves purposefully gathering and organizing data to create individual student learning profiles with. We administer these profiles in order to get to know our learners better, which then allows us to plan instruction and hence: differentiate. Learning profiles help us understand our students’ multiple intelligence strengths, their learning styles, what prior knowledge they have about a subject, what they’re interested in, how ready they are to learn something, what they are most challenged by, and what their learning limitations are if any.
Kolb’s research (1999) determined that we take in information through our senses, and some of us use more of one sense than another. Like our DNA, everyone’s sense and degree of sense used to interpret information varies. Seeing, hearing, speaking, smelling – our sense communicate information to our brains, and then share one dominant modality across the spectrum with which to best interpret and articulate information. Visual, auditory, and kinesthetic are all learning styles with specific characteristics. Here are some of them:
Visual Learner:
- Observe rather than act or speak
- Likes to read
- Uses graphics and/or pictures to memorize information
- Not easily distracted
- Struggles with only verbal instruction
- Uses good handwriting
- The Auditory Learner
- Enjoys reading aloud
- Enjoys speaking and verbally articulating
- Has difficulty with only written directions
- Likes to be read to
- Easily distracted by noise
- Is outgoing
- Enjoys listening
The Kinesthetic Learner:
- Enjoys problem solving and is generally good at it
- Problem solves using hands-on means
- Responds well to physical rewards
- Reading takes a back seat to hands-on activities
- Likes to try new things
- Taps a pencil or feet when reading or studying
Teaching to Interest, Preference, Culture, and Gender include the following:
- Topics or pursuits that evoke curiosity and passion in a learner; facets of learning that invite time and energy in pursuit of knowledge.
- Attributes that describe how a student learns best, to include learning style, intelligence preference, culture, and gender.
- Learning profiles to determine learning styles
- Preferences for learning are shaped by multiple and overlapping student factors that include learning style, intelligence, preference, culture, and gender.
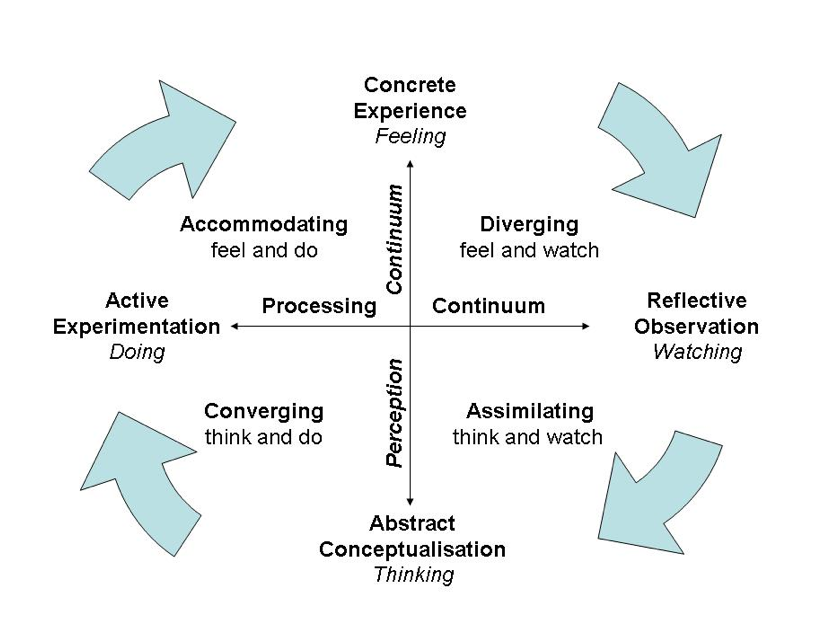
Kolb’s Learning Styles and Experiential Learning Model (1999)
Kolb studies of experiential learning have six main characteristics:
- Learning is best conceived as a process, not in terms of outcomes.
- Learning is a continuous process grounded in experience.
- Learning requires the resolution of conflicts between opposing modes of adaptation to the world (learning is by its very nature full of tension).
- Learning is a holistic process of adaptation to the world.
- Learning involves transactions between the person and the environment.
- Learning is the process of creating knowledge that is the result of the transaction between social knowledge and personal knowledge.
Experiential learning has implications for all learners. Kolb's learning theory is based on a four-stage learning cycle, distinguishing it from individual learning style inventories. Each achieves the same in the end: data about how our students learn best, and under what circumstances for optimal differentiation.
